Innovations
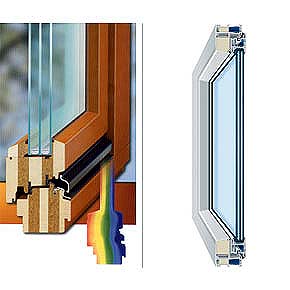
Innovations are made by either industry or research on any of the building components. The here listed innovations may not cover the whole area of new materials or applications, but shall give insight in what is ready to apply at buildings to be renovated. Windows Besides three-pane glazings for cold climates, the producers have spent development work on improved frames. Frames that include an insulation layer between wood or inside the plastic frame can reduce the frame-U-value down to 1.0 W/mēK. Another recent development is the improved spacer. Today most window glazing manufacturers use 0.4 mm galvanised steel for spacers but in a few cases insulating spacers are used, primarily to avoid condensation on the interior of the pane, sometimes the energy aspect leads to the use of improved spacers.

|
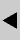  
|
|
Insulation material Graphite embedded expanded polystyrene (Neopor): To reduce the transmission losses of EPS material a solution was developed which embedded graphite material in the porous which results to a reduction in the radiant heat transfer within the material. With this technology it is possible to reduce the conductivity of the material about 20 %. Graphite embedded in EPS allows for achieving a comparable insulation effect with very low density level. Compared to conventional EPS less than half of the raw material is needed to achieve the same resulting insulation effect. Vacuum insulation systems: A new application of vacuum evacuated building elements is developed from the insulation industry. The thermal conductivity of this material is reduced by more than factor 10 compared to conventional material. This leads to much slimmer constructions of high performance houses. The evacuated silica gel material is covered by a high performance aluminium foil. The gas pressure in the construction is app. 1 mbar, the leakage rate is predicted to be below 2 mbar per year. To make the units applicable to construction conditions, the elements are glowed into a polystyrene cover. Thus the material is to be mostly protected to any sharp edge during transport or mounting. Other disadvantages are that the construction has to be produced industrial in size, no change of cutting it at the site is possible plus the price, which can be more than 10 times as high as conventional materials.
|